Konference Excel@FIT, která bude probíhat ve čtvrtek 25. 4. 2019 na Fakultě informačních technologií VUT v Brně, představí přijaté autorské práce a prezentační instalace sponzorů z oblasti IT.

V hlavním sále konference zazní odborné referáty autorů, kteří byli vybráni programovým výborem Excel@FIT a proběhne panelová diskuze na vybrané téma.

V určených prostorách konference proběhne volná přehlídka všech soutěžních prací formou plakátů a prototypů a prezentační instalace hostů.

V hlavním sále konference bude vyhlášení nejlepších prací a předání cen.
| 8.53 | Zahájení |
|---|---|
| 9.00 | Přednášky |
| 11.15 | Přestávka |
| 11.30 | Panelová diskuze |
| 12.30 | Oběd a networking |
| 13.30 | Přehlídka studentských prací formou plakátů a prototypů |
| 15.30 | Přestávka |
| 16.00 | Slavnostní vyhlášení výsledků a předání cen |
| 12:00-16:00 | Prezentace sponzorů a výzkumných skupin (foyer D, C a prostory Přehlídky) |
|---|

V dopoledním bloku budou v hlavním sále konference autoři vybraných prací prezentovat své výsledky.
Son Hai Nguyen
Augmented Reality, Computer Vision, Image Processing
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Augmented reality visualizes additional information in real-world environment. Main goal is achieving natural looking of the inserted 2D graphics in a scene captured by a stationary camera with possibility of real time processing. Although several methods tackled foreground segmentation problem, many of them are not robust enough on diverse datasets. Modified background subtraction algorithm ViBe yields best visual results, but because of the nature of binary mask, edges of the segmented objects are coarse. In order to smooth edges, Global Sampling Matting is performed, this refinement greatly increased the perceptual quality of segmentation. Considering that the shadows are not classified by ViBe, artifacts were occurring after insertion of segmented objects on top of the graphics. This was solved by the proposed shadow segmentation, which was achieved by comparing the differences between brightness and gradients of the background model and the current frame. To remove plastic look of the inserted graphics, texture propagation has been proposed, that considers the local and mean brightness of the background. Segmentation algorithms and image matting algorithms are tested on various datasets. Resulted pipeline is demonstrated on a dataset of videos.
Ondřej Valeš
finite automata, tree automata, language equivalence, language inclusion, bisimulation, antichains, bisimulation up-to congruence
Testování, analýza a verifikace
Tree automata and their languages find use in the field of formal verification and theorem proving but for many practical applications performance of existing algorithms for tree automata manipulation is unsatisfactory. In this work a novel algorithm for testing language equivalence and inclusion on tree automata is proposed and implemented as a module of the VATA library with a goal of creating algorithm that is comparatively faster than existing methods on at least a portion of real-world examples. First, existing approaches to equivalence and inclusion testing on both word and tree automata are examined. These existing approaches are then modified to create the bisimulation up-to congruence algorithm for tree automata. Efficiency of this new approach is compared with existing tree automata language equivalence and inclusion testing methods.

Pavel Hřebíček
Mobilní aplikace, Eye Check, Leukokorie, Zdravé oči, iOS, Android, React Native, OpenCV, Dlib, REST
Uživatelská rozhraní Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Cílem této práce je návrh a implementace multiplatformní multijazyčné mobilní aplikace pro rozpoznání leukokorie ze snímku lidského obličeje pro platformy iOS a Android. Leukokorie je bělavý svit zornice, který se při použití blesku může na fotografii objevit. Včasnou detekcí tohoto symptomu lze zachránit zrak člověka. Samotná aplikace umožňuje analyzovat fotografii uživatele a detekovat přítomnost leukokorie. Cílem aplikace je tedy analýza očí člověka, od čehož je také odvozen název mobilní aplikace - Eye Check. K vytvoření multiplatformní aplikace byl použit framework React Native. Pro detekci obličeje a práci s fotografií byly použity knihovny OpenCV a Dlib. Komunikace mezi klientem a serverem je řešena pomocí architektury REST. Výsledkem je mobilní aplikace, která při detekci leukokorie uživatele upozorní, že by měl navštívit svého lékaře.

Drahomír Dlabaja
Light field, Lossy compression, JPEG, Transform coding, Plenoptic representation, Quality assessment
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
This paper proposes a light field image encoding solution based on four-dimensional discrete cosine transform and quantization. The solution is an extension to JPEG baseline compression. A light field image is interpreted and encoded as a four-dimensional volume to exploit both intra and inter view correlation. Solutions to 4D quantization and block traversal are introduced in this paper. The experiments compare the performance of the proposed solution against the compression of individual image views with JPEG and HEVC intra in terms of PSNR. Obtained results show that the proposed solution outperforms the reference encoders for light images with a low average disparity between views, therefore is suitable for images taken by lenslet based light field camera and images synthetically generated.

Nikola Valešová
Machine learning, Metagenomics, Bacteria classification, Phylogenetic tree, 16S rRNA, DNA sequencing, scikit-learn
Bioinformatika
This work deals with the problem of automated classification and recognition of bacteria after obtaining their DNA by the sequencing process. In the scope of this paper, a~new classification method based on the 16S rRNA gene segment is designed and described. The presented principle is based on the tree structure of taxonomic categories and uses well-known machine learning algorithms to classify bacteria into one of the connected classes at a~given taxonomic level. A~part of this work is also dedicated to implementation of the described algorithm and evaluation of its prediction accuracy. The performance of various classifier types and their settings is examined and the setting with the best accuracy is determined. Accuracy of the implemented algorithm is also compared to an existing method based on BLAST local alignment algorithm available in the QIIME microbiome analysis toolkit.
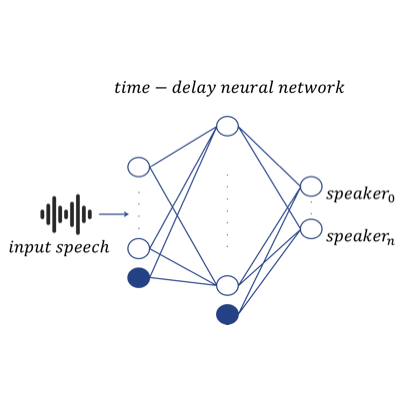
Ján Profant
speaker verification, neural networks, deep learning
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
The objective of this work is to study state-of-the-art deep neural networks based speaker verification systems called x-vectors on wideband conditions, such as YouTube. This system takes variable length audio recording and maps it into fixed length embedding which is afterward used to represent the speaker. We compared our systems to BUT's submission to Speakers in the Wild Speaker Recognition Challenge (SITW). We observed, that when comparing single best systems, with recently published x-vectors we were able to obtain more than 4.38 times lower Equal Error Rate on SITW core-core condition compared to SITW submission from BUT. Moreover, we find that diarization substantially reduces error rate when there are multiple speakers for SITW core-multi condition but we could not see the same trend on NIST Speaker Recognition Evaluation 2018 Video Annotations for YouTube data.
Jan Kohút
rozpoznávání textu, rekurentní neuronové sítě, konvoluční neuronové sítě, adaptace, aktivní učení, dataset IMPACT
Robotika a umělá inteligence Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Cílem této práce je srovnání architektur neuronových sítí pro rozpoznávání textu. Dále pak adaptace neuronových sítí na jiné texty, než na kterých byly učeny. Pro tyto experimenty využívám rozsáhlý a rozmanitý dataset IMPACT o více než jednom milionu řádků. Pomocí neuronových sítí provádím kontrolu vhodnosti řádků tzn. čitelnost a správnost výřezů řádků. Celkem srovnávám 6 čistě konvolučních sítí a 9 rekurentních sítí. Adaptace provádím na polských historických textech s~tím, že trénovací data adaptovaných sítí neobsahovaly texty ve slovanských jazycích. Adaptace využívají přístupy aktivního učení pro výběr nových adaptačních dat. Čistě konvoluční sítě dosahují úspěšnosti 98.6 \%, rekurentní sítě pak 99.5 \%. Úspěšnost sítí před adaptací se pohybuje kolem 79\%, po postupné adaptaci na 2500 řádcích stoupne úspěšnost na 97 \%. Přístupy aktivního učení dosahují lepší úspěšnosti než náhodný výběr. Pro zpracování datasetů je vhodné používat již natrénované neuronové sítě tak, aby se odstranilo co možná nejvíce chybných dat. Rekurentní vrstvy znatelně zvyšují úspěšnost sítí. Při adaptaci je výhodné využívat přístupů aktivního učení.

Josef Jon
neural machine translation, context, transformer, document level translation
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
This works explores means of utilizing extra-sentential context in neural machine translation (NMT). Traditionally, NMT systems translate one source sentence to one target sentence without any notion of surrounding text. This is clearly insufficient and different from how humans translate text. For many high resource language pairs, NMT systems output is nowadays indistinguishable from human translations under certain (strict) conditions. One of the conditions is that evaluators see the sentences separately. When evaluating whole documents, even the best NMT systems still fall short of human translations. This motivates the research of employing document context in NMT, since there might not be much more space left to improve translations on sentence level, at least for high resource languages and domains. This work sumarizes recent state-of-the art approaches, implements them, evaluates them both in terms of general translation quality and on specific context related phenomena and analyzes their shortcomings. Additionaly, context phenomena test set for English to Czech translation was created to enable further comparison and analysis.

Martin Vondráček
Network Traffic Analysis, Reverse Engineering, Application Crippling, Penetration Testing, Hacking, Social Applications, Unity, Bigscreen, HTC Vive, Oculus Rift
Bezpečnost Počítačové sítě
Immersive virtual reality is a technology that finds more and more areas of application. It is used not only for entertainment but also for work and social interaction where user's privacy and confidentiality of the information has a high priority. Unfortunately, security measures taken by software vendors are often not sufficient. This paper shows results of extensive security analysis of a popular VR application Bigscreen which has more than 500,000 users. We have utilised techniques of network traffic analysis, penetration testing, reverse engineering, and even application crippling. We have found critical vulnerabilities directly exposing the privacy of the users and allowing the attacker to take full control of a victim's computer. Found security flaws allowed distribution of malware and creation of a botnet using a computer worm. Our team has discovered a novel VR cyber attack Man-in-the-Room. We have also found a security vulnerability in the Unity engine. Our responsible disclosure has helped to mitigate the risks for more than half a million Bigscreen users and all affected Unity applications worldwide.

Patrik Goldschmidt
TCP Reset Cookies, TCP SYN Flood, DDoS mitigation
Počítačové sítě
TCP SYN Flood is one of the most widespread DoS attack types used on computer networks nowadays. As a possible countermeasure, this paper proposes a long-forgotten network-based mitigation method TCP Reset Cookies. The method utilizes the TCP three-way-handshake mechanism to establish a security association with a client before forwarding its SYN data. Since the nature of the algorithm requires client validation, all SYN segments from spoofed IP addresses are effectively discarded. From the perspective of a legitimate client, the first connection causes up to 1-second delay, but all consecutive SYN traffic is delayed only by circa 30 microseconds. The document provides a detailed description and analysis of this approach, as well as implementation details with enhanced security tweaks. The project was conducted as a part of security research by CESNET. The discussed implementation is already integrated into a DDoS protection solution deployed in CESNET's backbone network and Czech internet exchange point at NIX.CZ.

Daniel Uhříček
IoT, Malware, Linux, Security, Dynamic Analysis, Network Analysis, SystemTap
Bezpečnost
Weak security standards of IoT devices levereged Linux malware in past few years. Exposed telnet and ssh services with default passwords, outdated firmware or system vulnerabilities -- all of those are ways of letting attackers build botnets of thousands of compromised embedded devices. This paper emphasizes the importance of open source community in the field of malware analysis and presents design and implementation of multiplatform sandbox for automated malware analysis on Linux platform. Project LiSa (Linux Sandbox) is a modular system which outputs json data that can be further analyzed either manually or with pattern matching (e.g. with YARA) and serves as a tool to detect and classify Linux malware. LiSa was tested on recent IoT malware samples provided by Avast Software and it solved various problems of existing implementations.

Dominik Harmim, Vladimír Marcin, Ondřej Pavela
Facebook Infer, Static Analysis, Abstract Interpretation, Atomicity Violation, Concurrent Programs, Performance, Worst-Case Cost, Deadlock
Testování, analýza a verifikace
Static analysis has nowadays become one of the most popular ways of catching bugs early in the modern software. However, reasonably precise static analyses do still often have problems with scaling to larger codebases. And efficient static analysers, such as Coverity or Code Sonar, are often proprietary and difficult to openly evaluate or extend. Facebook Infer offers a static analysis framework that is open source, extendable, and promoting efficient modular and incremental analysis. In this work, we propose three inter-procedural analysers extending the capabilities of Facebook Infer: Looper (a resource bounds analyser), L2D2 (a low-level deadlock detector), and Atomer (an atomicity violation analyser). We evaluated our analysers on both smaller hand-crafted examples as well as publicly available benchmarks derived from real-life low-level programs and obtained encouraging results. In particular, L2D2 attained 100 % detection rate and 11 % false positive rate on an extensive benchmark of hundreds of functions and millions of lines of code.