Juraj Holub
Blockchain, Proof-of-Stake, Harmony, Simulácia
Bezpečnost Modelování a simulace
V súčasnosti je blockchain populárnou technológiou používanou v distribuovaných aplikáciach, ktoré kladú dôraz na bezpečnosť (napríklad kryptomeny alebo elektronické voľby). Neustále prebieha vývoj nových blockchain protokolov s novými vlastnosťami. Vzhľadom na ich finančnú citlivosť je potrebné tieto nové protokoly podrobne preveriť z hľadiska bezpečnosti a výkonnosti ešte pred ich nasadením. Prirodzene sa pre tento účel naskytá simulácia. Cieľom tejto práce je simulovať blockchain protokol Harmony, ktorý poskytuje vysokú priepustnosť transakcií nezávisle od veľkosti siete. Simulácia sa zameriava na konsenzus protokol použitý v tomto blockchaine. Simulované boli konkrétne útoky na konsenzus ako aj všeobecná efektívnosť protokolu. Výsledky simulácie poukazujú na bezpečnostné riziko v podobe DDoS útoku. Na druhej strane, simulácia potvrdila vysokú priepustnosť transakcií pomocou mechanizmu sharding, a to bez výrazného zníženia bezpečnosti. Na záver je navrhnutá a odsimulovaná modifikácia protokolu, ktorá znižuje zraniteľnosť voči DDoS útoku. Čitateľ tejto práce sa oboznámi s posledným vývojom v technológii blockchain. Vytvorený nástroj môže poslúžiť ako základ pre simuláciu ďalších protokolov.
Sabína Gulčíková
finite memory automata, register automata, regular expression matching
Testování, analýza a verifikace
Register automaton (RA) operating over an infinite alphabet is one of the great tools for pattern matching with backreferences, runtime verification, or modelling of parallel computation. In case of pattern matching with backreferences, the state-of-the-art matchers make use of backtracking algorithms, whose application causes significant slowdown in case of nondeterministic regular expressions. The RA's property of non-determinisability makes it an unsuitable model for solution to problems related to inefficient usage of backtracking algorithms. On the other hand, the RA's quality of being equipped by a finite memory serves as a~good basis for storing the so-called capture groups used in this application. In this work, a~formal model called register set automaton is proposed. A large class of RAs can be transformed into this deterministic model, which, among other things, allows for fast pattern matching with backreferences. In this paper, we explore its properties including determinisability, expressive power, and closure under Boolean operations. In addition, algorithms for other problems, such as emptiness testing, are introduced.

Tomáš Hladký
Simulator, DAG-based consensus, Blockchain, Optimizations, Payoff function, Transaction throughput
Bezpečnost
We study existing Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) blockchain designs that propose to solve a blockchains throughput problem, especially protocols PHANTOM and its optimization GHOSTDAG. They utilize a Bitcoin protocol and propose a random transaction selection, resulting in increased transaction throughput. However, it has been proved by a simulation that actors that use the random transaction selection strategy have less profit than actors who do not follow the protocol and select transactions rationally (i.e., most profitable). That proof has been made on a small network of ten nodes with a circle topology. This article aims to extend, optimize, and automate an existing blockchain simulator. We implement a Bitcoin-like network topology with realistic block propagation latency. Furthermore, we optimize the simulator to run more simulations in parallel and faster, including automation tools that can create or edit input configurations, perform a combination of runs on multiple CPUs based on input parameters, and analyze profits and transaction collisions. Finally, we perform experiments to verify malicious actors' advantages in a Bitcoin-like network and create a payoff function to punish this behavior.

Barbora Šmahlíková
Büchi Automata, Elevator Automata, Büchi Complementation
Testování, analýza a verifikace
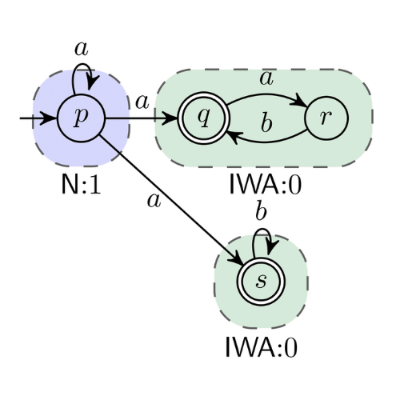
Büchi automata complementation is an important operation for decision procedures of some logics, proving termination of programs, or model checking of temporal properties. Due to the high space complexity of Büchi automata complementation, it is necessary to look for some optimizations reducing the size of generated state space for good performance in practice. In this paper, we identify elevator automata, a class of Büchi automata, which often occurs in practice. Thanks to their specific structure, we are able to reduce the bound on the maximum rank of states in each strongly connected component, which is one of the main causes of a state space blow-up in rank-based complementation. We compare these techniques, implemented as an extension of the tool Ranker, with other state-of-the-art tools and show that with these optimizations, rank-based complementation is competitive to other complementation approaches and can give better results on a large set of benchmarks.
Tomáš Dacík
Logic, Separation Logic, Decision Procedure
Testování, analýza a verifikace
Separation logic (SL) is one of the most successful tools for verification of programs that manipulate dynamically allocated memory. Its expressive power comes at a cost of undecidability when several of its features, namely negation, inductive predicates describing data structures and separating implications are combined. To circumvent this problem, the recently introduced strong-separation logic (SSL) uses a stricter definition of the semantics, making it decidable, while remaining suitable for verification. However, there is currently no implementation of a decision procedure for SSL. In this work, we propose a decision procedure for SSL based on a translation to first-order formulae that can be later solved by a specialized solver. Our preliminary experimental results show that our approach can effectively solve formulae obtained from verification tools based on SL and also outperform existing decision procedure based on similar translation.

Son Hai Nguyen
neural solver, Helmholtz equation, graph neural network, transcranial ultrasound, PDE
Modelování a simulace Robotika a umělá inteligence
Neural solvers have been increasingly explored with the aim of replacing computationally expensive conventional numerical methods for solving PDEs. This work focuses on solving the time-independent Helmholtz equation for transcranial ultrasound therapy. Most of the popular methods for modeling physics systems are based on U-net. However, convolutional neural networks require the data to be sampled on a regular grid. In order to try to lift this restriction, we propose an iterative solver based on graph neural networks. Unlike Physics-informed neural networks, our model needs to be trained only once, and only a forward pass is required to obtain a new solution given input parameters. The model is trained using supervised learning, where the reference results are computed using the traditional solver k-Wave. Our results show the model’s unroll stability despite being trained with only 8 unroll iterations. Despite the model being trained on the data with a single source, it can predict wavefields with multiple sources and generalize to much larger computational domains. Our model can produce a prediction for sub-pixel points with higher accuracy than linear interpolation.

Martin Zaťovič
autofocus, tekutá šošovka, kamera, zaostrovanie, spracovanie obrazu
Počítačová architektura a vestavěné systémy Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Rýchlosť zaužívaného prístupu k zaostrovaniu kamerových systémov naráža na úzke hrdlo - mechanický pohyb motora, ktorý mení vzdialenosť šošovky od snímaného objektu. Tento pohyb spomaľuje zaostrovanie, ktoré je v mnohých prípadoch kritická operácia zariadení, ktoré využívajú kamerový systém, pretože vzniká potreba vyčkávať na správne zaostrenie. Riešenie predstavuje inovatívna technológia tekutej šošovky. Tekutá šošovka eliminuje potrebu mechanického pohybu a vďaka tomu je schopná takéto systémy urýchliť. Budeme sa venovať overeniu rýchlosti tejto technológie, jej výhodám a nevýhodám a ukážeme si jej využitie na príkladoch z reálneho sveta. Ideálnym príkladom pre využitie tekutej šošovky sú zariadenia, ktoré často preostrujú - hĺbkový skener, alebo linka, ktorá sníma štítky s textom na balíkoch rôznej veĺkosti.

Jan Zbořil
IoT, IoT gateways, network traffic analysis, attacks on IoT devices
Bezpečnost Počítačové sítě
Modern IoT gateways are mainly developed by private companies behind closed doors. This results in a closed ecosystem, where only a small amount of information about traffic is available to the public. Therefore, to gain knowledge regarding the operation and communication of such gateways, it is necessary to examine and analyse network traffic flowing to and fro such gateways. This paper's primary goal is to capture and process network traffic data of multiple commercially available gateways intended for home use, analyse their communication behaviours, compare the results to other studies carried out in this area, and discuss possible attacks on used gateways based on gathered data. Communication data were obtained by deploying a controlled environment and analysed using Zeek, together with Wireshark software. Gathered communication data can be further used by researchers in the areas of networking or security.
Jindřich Šesták
ESP32, ESP-NOW, Mesh network, Mesh, Espressif, MicroPython, Asyncio
Počítačové sítě
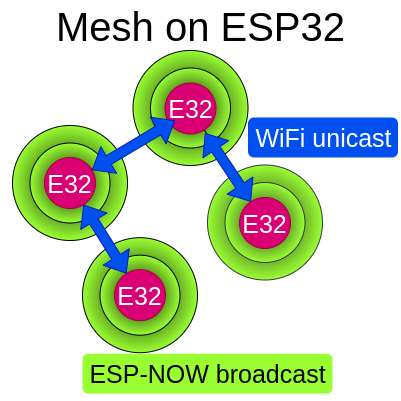
The aim of this project is to implement a mesh network protocol on ESP32 microchips in MicroPython. It mainly focuses on the functioning of mesh in two modes, with connection to the Internet and without it. This thesis was ordered by Espressif company for improving and discovering new ways of mesh networking. % The solution of this mesh network uses two network protocols. First, the ESP-NOW protocol offers low power consumption and doesn't need any network connection. The second is the common WiFi protocol which is used for data transmission. WiFi links are formed between ESP32 nodes and one of the nodes can even be connected to the Internet and offer a connection to the whole mesh. % With full functionality, the mesh will be light weighted and will connect multiple nodes. It is possible to run user applications like light control on ESP32 boards on top of the mesh using WiFi. With WiFi, it is possible to transfer big amount of data for applications. The work is still in progress. % In this project, there are used new innovations to ensure the formation of a structure in the mesh. The problem of how to select a root node in an environment without the WiFi Access Point (Router, AP) is presented.
Petr Kohout
bioinformatika, proteinové inženýrstvı́, molekulárnı́ dynamika, tunely, dokovánı́
Tato práce se zabývá analýzou proteinových struktur. Cílem je vytvořit Caver Web 2.0 - novou verzi webové aplikace, která začlení další vědecké nástroje a uživatelům umožní projít komplikovaný pracovní protokol za poskytnutí relevantních výsledků bez nutnosti hlubší znalosti integrovaných nástrojů. Vše bude zprostředkováno prostřednictvı́m jednoduchého a interaktivnı́ho uživatelského rozhranı́. Aplikace rozšiřuje původnı́ aplikaci Caver Web 1.0 o nové vlastnosti. Caver Web 1.0 je webový server vhodný pro identifikaci proteinových tunelů a kanálů, pro které umožňuje spustit analýzy transportu ligandů. Program se vyznačuje intuitivnı́m a uživatelsky přı́větivým rozhranı́m s minimem požadovaných vstupů od uživatele. Server je vhodný i pro výzkumnı́ky bez pokročilých bioinformatických nebo technických znalostı́. Jeho současná verze je ve vědecké komunitě dobře zavedená a velmi využı́vaná (35 000 dokončených výpočtů během dvou let provozu). Nejvýznamnějšı́m omezenı́m současné verze je možnost analyzovat pouze statickou strukturu, což často poskytuje neúplný biologický obraz. Proto jsme se rozhodli nástroj rozšı́řit o výpočet molekulárnı́ch dynamik, které poskytnou ucelený obraz na proměny proteinových struktur. Touto funkcı́ se Caver Web 2.0 stane prvnı́m webovým nástrojem, který bude poskytovat analýzu tunelů bez nutnosti ručnı́ch výpočtů molekulárnı́ch dynamik. Grafické uživatelské rozhranı́ bude navrženo speciálně pro vědeckou komunitu s podporou jednoduchého exportu. Nástroj bude zdarma k dispozici celé vědecké komunitě.

Jan Zavřel
BGP, simulation, routing protocol, OMNeT++, INET
Modelování a simulace Počítačové sítě
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) was first sketched on two napkins over a conference lunch in 1989 by two gentlemen, and it would become one of, if not the most, essential routing protocols of our time in just a few years. It creates the global routing system of the Internet. Billions of people rely on BGP every single day without even knowing about it. A recent example of our collective reliance on BGP takes us back a few months ago when Facebook engineers misconfigured their BGP instances, effectively cutting themselves off from the outside. The global importance of this protocol led to the creation of this paper, which discusses improvements to the BGP simulation model. Such a model, if of high quality, could help network engineers and others test the stability of their topologies and configurations inside a safe discrete environment. The model, written in C++, is improved and extended in several directions with new features, such as full support for the IPv6 address family, Cisco-like configuration, the BGP table, TCP improvements, and many more. The quality of the model is ensured by a close comparison of all aspects of the model to Cisco's implementation of BGP.

Nemanja Vasiljević
Event, Notifications, OpenStack Swift
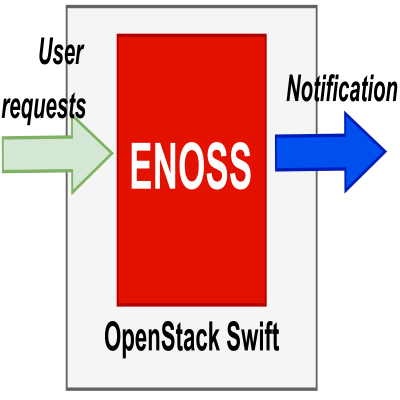
Currently, object storage OpenStack Swift does not provide any pieces of information to users about events that occurred in storage they own/have access to. For example, users do not have information when the content of their object storage is accessed, changed, created, or deleted. This paper aims to create a solution that will send notifications about events that occurred in OpenStack Swift to user-specified destinations. The proposed solution, using metadata, allows users to specify where and which event should be published based on even types (read, create, modify, delete) and other properties such as object prefix, suffix, size. It also offers multiple destinations(Beanstalkd queue, Kafka, etc.) to which notifications can be published. The solution is fully compatible with AWS S3 Event Notifications and, compared to AWS, supports more destinations, event types, filters and allows unsuccessful events to be published. Event notification can be used for monitoring, automatization, and serverless computing (similar to AWS Lambda).
Dominik Boboš
Detection of re-occurring sequences in audio, Segmental dynamic time warping, Recurrence quantification analysis, Fuzzy string matching, Bottleneck features, Phoneme posteriors
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Recognition of pre-recorded messages in speech such as "This number is not reachable" is useful for any follow-up speech data mining. To investigate the identification of redundant information in audio, it is necessary to have a large amount of data with the exact phrases repeated multiple times. Such a set is generated by mixing pre-recorded messages into phone calls with variations in speed, volume and repetitions. The created system tackles “known messages” and “unknown messages” scenarios by using approaches like clustering or detection in chunks. Dynamic time warping, approximate string matching and recurrent quantification analysis are compared, and finally, all mentioned techniques are combined to obtain a precise and efficient system.

Samuel Repka
Photometric stereo, Scanning electron microscope, 4-segment BSE detector
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
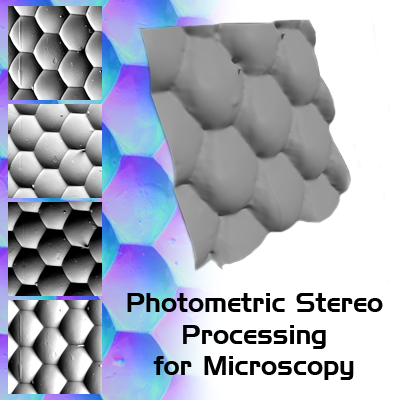
While scanning electron microscopes (SEM) provide an extraordinary spectrum of information about the specimens, they do not answer a few fundamental questions. How high? How deep? This paper aims to explore possibilities of topography reconstruction of microscopic samples, as well as to attempt to solve the task using tools already available on conventional scanning electron microscopes. The proposed solution uses images from a four-segment backscattered electrons detector as an input to the photometric stereo algorithm. This algorithm exploits the fact, that the brightness of the image point is dependent on the inclination of the sample surface. Reflectance maps are used to estimate the inclination in each pixel, creating a map of normal vectors. The map is then used for topography reconstruction. A novel technique for reflectance map estimation is proposed. This method is applied to tin samples to remove the sample’s atomic number effects. Solution evaluation was not yet performed. The fact that all data are acquired simultaneously allows for fast reconstruction. Usage of already available and widespread tools eliminate a need for specialized equipment such as Atomic Force Microscopes.
Michael Holubec
Reading order, Posloupnost čtení, Prostorová analýza, Jazyková analýza, Jazykový model, LSTM, OCR
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
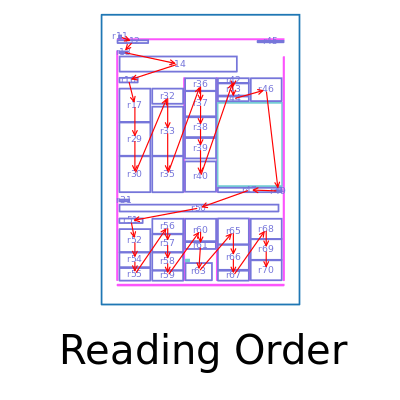
Práce se zabývá stanovením posloupnost čtení (Reading order) textových regionů u digitalizovaných dokumentů. Identifikace posloupnosti čtení je jednou z důležitých součástí při rekonstrukci a extrakci obsahu digitalizovaných dokumentů. Kromě zavedených metod využívajících k sestavení posloupností čtení prostorových informací, práce zkoumá také možnost využití textového obsahu dokumentu a jeho analýzy pomocí jazykového modelu. Na datasetu třinácti novinových článků porovnává úspěšnost identifikace správné posloupnosti čtení pomocí prostorové analýzy, jazykové analýzy a kombinované analýzy. Prostorová analýza dle provedených experimentů dosahuje 85 % úspěšnosti. Samotný jazykový model poskytuje velmi omezené výsledky (úspěšnost 16 %), jeho užití v kombinaci s prostorovou analýzou však zvyšuje úspěšnost z původních 85 % na 89 %. Výstupem práce jsou mechanismy identifikující posloupnost čtení, které mohou sloužit pro dodatečné zpracování digitalizovaných dokumentů. Rovněž poskytují robustní základ pro případná další rozšíření a vylepšení přesnosti identifikace posloupnosti čtení.
Samuel Repka
Photometric stereo, Scanning electron microscope, 4-segment BSE detector
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
While scanning electron microscopes (SEM) provide an extraordinary spectrum of information about the specimens, they do not answer a few fundamental questions. How high? How deep? This paper aims to explore possibilities of topography reconstruction of microscopic samples, as well as to attempt to solve the task using tools already available on conventional scanning electron microscopes. The proposed solution uses images from a four-segment backscattered electrons detector as an input to the photometric stereo algorithm. This algorithm exploits the fact, that the brightness of the image point is dependent on the inclination of the sample surface. Reflectance maps are used to estimate the inclination in each pixel, creating a map of normal vectors. The map is then used for topography reconstruction. A novel technique for reflectance map estimation is proposed. This method is applied to tin samples to remove the sample’s atomic number effects. Solution evaluation was not yet performed. The fact that all data are acquired simultaneously allows for fast reconstruction. Usage of already available and widespread tools eliminate a need for specialized equipment such as Atomic Force Microscopes.

Dominik Boboš
Detection of re-occurring sequences in audio, Segmental dynamic time warping, Recurrence quantification analysis, Fuzzy string matching, Bottleneck features, Phoneme posteriors
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Recognition of pre-recorded messages in speech such as "This number is not reachable" is useful for any follow-up speech data mining. To investigate the identification of redundant information in audio, it is necessary to have a large amount of data with the exact phrases repeated multiple times. Such a set is generated by mixing pre-recorded messages into phone calls with variations in speed, volume and repetitions. The created system tackles “known messages” and “unknown messages” scenarios by using approaches like clustering or detection in chunks. Dynamic time warping, approximate string matching and recurrent quantification analysis are compared, and finally, all mentioned techniques are combined to obtain a precise and efficient system.

Son Hai Nguyen
neural solver, Helmholtz equation, graph neural network, transcranial ultrasound, PDE
Modelování a simulace Robotika a umělá inteligence
Neural solvers have been increasingly explored with the aim of replacing computationally expensive conventional numerical methods for solving PDEs. This work focuses on solving the time-independent Helmholtz equation for transcranial ultrasound therapy. Most of the popular methods for modeling physics systems are based on U-net. However, convolutional neural networks require the data to be sampled on a regular grid. In order to try to lift this restriction, we propose an iterative solver based on graph neural networks. Unlike Physics-informed neural networks, our model needs to be trained only once, and only a forward pass is required to obtain a new solution given input parameters. The model is trained using supervised learning, where the reference results are computed using the traditional solver k-Wave. Our results show the model’s unroll stability despite being trained with only 8 unroll iterations. Despite the model being trained on the data with a single source, it can predict wavefields with multiple sources and generalize to much larger computational domains. Our model can produce a prediction for sub-pixel points with higher accuracy than linear interpolation.

Tomáš Hladký
Simulator, DAG-based consensus, Blockchain, Optimizations, Payoff function, Transaction throughput
Bezpečnost
We study existing Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) blockchain designs that propose to solve a blockchains throughput problem, especially protocols PHANTOM and its optimization GHOSTDAG. They utilize a Bitcoin protocol and propose a random transaction selection, resulting in increased transaction throughput. However, it has been proved by a simulation that actors that use the random transaction selection strategy have less profit than actors who do not follow the protocol and select transactions rationally (i.e., most profitable). That proof has been made on a small network of ten nodes with a circle topology. This article aims to extend, optimize, and automate an existing blockchain simulator. We implement a Bitcoin-like network topology with realistic block propagation latency. Furthermore, we optimize the simulator to run more simulations in parallel and faster, including automation tools that can create or edit input configurations, perform a combination of runs on multiple CPUs based on input parameters, and analyze profits and transaction collisions. Finally, we perform experiments to verify malicious actors' advantages in a Bitcoin-like network and create a payoff function to punish this behavior.

Ján Pavlus
speech-separation, GAN, robust, adversarial augmentations
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Speech separation is a task of separating single signals from the given mixture of multiple speakers. Speech separation systems are trained on artificial mixtures generated from single speaker's signals. These signals are then used as targets for the training. Neural networks trained this way work well on artificial data but they often fail on real-world examples. To improve their behavior on real-world mixtures it is possible to use training data augmentations for example noise addition. Nevertheless, the power of these augmentations is limited as they have to be manually designed. Using generative adversarial networks (GAN) could improve this process by generating augmentations for data depending on the success of confusing the separation system using these data. Speech separation could be then made more and more robust with each generator and separator training step. This paper describes experiments that are used to find the right parameters and their combination for the GAN model training. Although the experiments do not yet lead to a more robust speech separation, they provide an analysis of the pitfalls of training the GAN, which is the necessary first step towards a successful system. These experiments show that training the GAN model to the stable state is difficult by adjusting the exact number of batches, after which the separator and generator training is switched. On the other hand, adjusting the to-be-achieved scores of the generator or separator training move could work much better and train the GAN model properly. Other experiments have to be done to prove the correctness of these parameters and their settings.
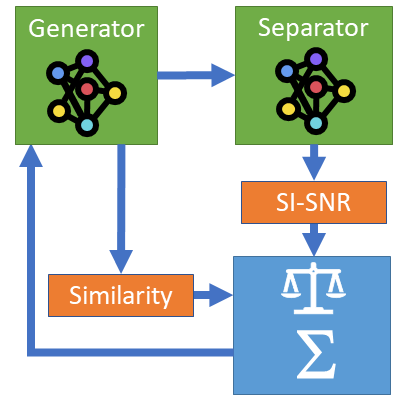
Timotej Kamenský
LTE, SDR, IMSI catcher, DoS, Downgrade Attack
Bezpečnost Počítačové sítě
This work strives to create an intrusive device targeting LTE networks. It should implement several already described attacks: IMSI catcher, downgrade attack, denial of service. These attacks are taking use of inherent weaknesses of the LTE protocol, which makes defending against them is hard. This goal should be achieved in a compact hardware package. The key piece of hardware is Software Defined Radio (SDR), namely Blade-RF 2.0. It is a general-purpose radio which allows us to work with radio technology through an abstract programming layer instead of relying on tinkering with hardware. The result of this work can serve the security community in penetration testing and researching security of mobile networks.

Adam Ferencz
dron, semiautonomní, simulace, AirSim, python, bezpečný let
Robotika a umělá inteligence Uživatelská rozhraní
Piloti dronu často musí hlídat při plnění průzkumné mise více věcí zároveň. Pilot něco pozoruje, sleduje obraz, natočení dronu, rychlost a překážky. Cílem této práce je vytvořit aplikaci, která pilotovi ulehčí hlídání bezpečné polohy dronu. Článek prezentuje novou metodu, která reviduje povely pilota tak, aby se dron držel "bezpečně blízko" předem definované dráze letu. Pilot se tak může více věnovat plnění cílů mise, než přímému a bezpečnému řízení dronu. Navržená metoda byla testována v aplikaci, která umožňuje definovat bezpečnou trajektorii dronu a pro testovací lety využívá integraci simulátoru. Výstupem jsou testy uživatelské aplikace v simulátoru AirSim, kde uživatel dělá nejdříve misi bez zapnuté korekce a poté s ní. V uživatelských testech, kde byl cíl splnit průzkumnou misi, piloti při letu bez korekce strávili 55% mimo definovanou bezpečnou oblast a při letu s asistentem takto strávili pouze 5%. Průměrné vychýlení zavedení od ideální trajektorie kleslo z 2,29 metrů na 0,92 metru (bezpečná vzdálenost byla při testech do 2 metrů).

Matej Viskupič
Sledovanie osôb, Identifikácia osôb, Heatmap of presence
Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Cieľom tejto práce je preskúmať možnosti a navrhnúť systém monitorovania návštevníkov muzejných expozícií. Na rozdiel od doterajších metód naše riešenia skúma využitie kamerovej technológie. Tento prístup priniesol tri podproblémy: (1.) detekciu ľudí v kamerovom zázname za pomoci konvolučnej neurónovej siete (2.) presné určenie polohy osôb v monitorovanom priestore za použitia externej konfigurácie kamier a (3.) identifikáciu detegovaných osôb. Výstupom nášho riešenia je štatistika návštevnosti jednotlivých expozícií, mapa znázorňujúca pohyb návštevníkov a tepelná mapa zobrazujúca čas strávený pred jednotlivými expozíciami. Tieto výstupy môžu prispieť k lepšiemu vyhodnocovaniu potrieb návštevníkov a k efektívnejšiemu výberu alebo rozmiestneniu exponátov.

Martin Zaťovič
autofocus, tekutá šošovka, kamera, zaostrovanie, spracovanie obrazu
Počítačová architektura a vestavěné systémy Zpracování dat (obraz, zvuk, text apod.)
Rýchlosť zaužívaného prístupu k zaostrovaniu kamerových systémov naráža na úzke hrdlo - mechanický pohyb motora, ktorý mení vzdialenosť šošovky od snímaného objektu. Tento pohyb spomaľuje zaostrovanie, ktoré je v mnohých prípadoch kritická operácia zariadení, ktoré využívajú kamerový systém, pretože vzniká potreba vyčkávať na správne zaostrenie. Riešenie predstavuje inovatívna technológia tekutej šošovky. Tekutá šošovka eliminuje potrebu mechanického pohybu a vďaka tomu je schopná takéto systémy urýchliť. Budeme sa venovať overeniu rýchlosti tejto technológie, jej výhodám a nevýhodám a ukážeme si jej využitie na príkladoch z reálneho sveta. Ideálnym príkladom pre využitie tekutej šošovky sú zariadenia, ktoré často preostrujú - hĺbkový skener, alebo linka, ktorá sníma štítky s textom na balíkoch rôznej veĺkosti.

Jindřich Šesták
ESP32, ESP-NOW, Mesh network, Mesh, Espressif, MicroPython, Asyncio
Počítačové sítě
The aim of this project is to implement a mesh network protocol on ESP32 microchips in MicroPython. It mainly focuses on the functioning of mesh in two modes, with connection to the Internet and without it. This thesis was ordered by Espressif company for improving and discovering new ways of mesh networking. % The solution of this mesh network uses two network protocols. First, the ESP-NOW protocol offers low power consumption and doesn't need any network connection. The second is the common WiFi protocol which is used for data transmission. WiFi links are formed between ESP32 nodes and one of the nodes can even be connected to the Internet and offer a connection to the whole mesh. % With full functionality, the mesh will be light weighted and will connect multiple nodes. It is possible to run user applications like light control on ESP32 boards on top of the mesh using WiFi. With WiFi, it is possible to transfer big amount of data for applications. The work is still in progress. % In this project, there are used new innovations to ensure the formation of a structure in the mesh. The problem of how to select a root node in an environment without the WiFi Access Point (Router, AP) is presented.

Dominik Müller
Hardware-in-the-loop, Simulace vestavěných systémů, Akcelerace vývoje
Počítačová architektura a vestavěné systémy Testování, analýza a verifikace
Tato práce se zabývá návrhem a realizací platformy, umožňující vývojáři definovat simulované prostředí vestavěného systému. Platforma umožňuje vývojáři vybrat nebo vytvořit zařízení, vyskytující se v okolí vyvíjeného systému a detailně definovat jejich parametry a chování. Simulace okolí mikrokontroléru je rozdělena na harwarovou úroveň a na úroveň deterministického real-time prostředí. Odpadají tak některé limitace softwarových řešení. Navrhovaná platforma představuje pohled na testování vestavěných systémů během ranných fazí vývoje. Tento pohled je odlišný od běžných řešení a snaží se tak zvýšit efektivitu vývojáře. Návrh platformy cílí na její snadnou rozšířitelnost, konfigurovatelnost a univerzalitu. Výstupem této práce je platforma demonstrující myšlenky uvedené v tomto článku, která slouží jako vhodný základ pro budoucí rozšíření.
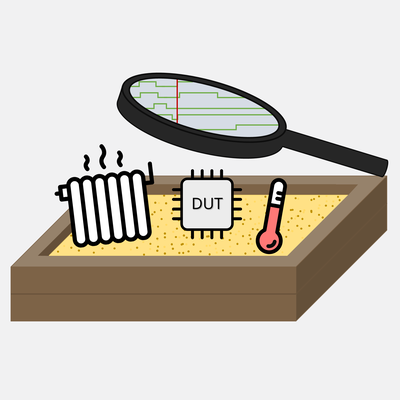
Ondřej Babec
MQTT, Async, Rust, Embedded, Industry4.0, Smart-home
Počítačová architektura a vestavěné systémy
The main target of this work is to create an asynchronous MQTT client, supporting MQTT version 5, in Rust running on embedded devices powered by Drogue device opensource firmware. The number of clients that support MQTT version 5 is highly limited, and currently, no client implementation exists in Rust. The main implementation challenge is that MQTT version 5 has properties of variable lengths. Storing these properties of size which is unknown during compile time is a massive obstacle because embedded Rust does not support dynamic allocation as there is no underlying operating system. The result of the work is a client that has comparable functionalities as other available clients in different languages. The client library is extended with both desktop and embedded async executors. Although the client could be used almost everywhere, the leading variants are Industry 4.0 and Smart home.

Son Hai Nguyen
neural solver, Helmholtz equation, graph neural network, transcranial ultrasound, PDE
Modelování a simulace Robotika a umělá inteligence
Neural solvers have been increasingly explored with the aim of replacing computationally expensive conventional numerical methods for solving PDEs. This work focuses on solving the time-independent Helmholtz equation for transcranial ultrasound therapy. Most of the popular methods for modeling physics systems are based on U-net. However, convolutional neural networks require the data to be sampled on a regular grid. In order to try to lift this restriction, we propose an iterative solver based on graph neural networks. Unlike Physics-informed neural networks, our model needs to be trained only once, and only a forward pass is required to obtain a new solution given input parameters. The model is trained using supervised learning, where the reference results are computed using the traditional solver k-Wave. Our results show the model’s unroll stability despite being trained with only 8 unroll iterations. Despite the model being trained on the data with a single source, it can predict wavefields with multiple sources and generalize to much larger computational domains. Our model can produce a prediction for sub-pixel points with higher accuracy than linear interpolation.

Jan Zavřel
BGP, simulation, routing protocol, OMNeT++, INET
Modelování a simulace Počítačové sítě
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) was first sketched on two napkins over a conference lunch in 1989 by two gentlemen, and it would become one of, if not the most, essential routing protocols of our time in just a few years. It creates the global routing system of the Internet. Billions of people rely on BGP every single day without even knowing about it. A recent example of our collective reliance on BGP takes us back a few months ago when Facebook engineers misconfigured their BGP instances, effectively cutting themselves off from the outside. The global importance of this protocol led to the creation of this paper, which discusses improvements to the BGP simulation model. Such a model, if of high quality, could help network engineers and others test the stability of their topologies and configurations inside a safe discrete environment. The model, written in C++, is improved and extended in several directions with new features, such as full support for the IPv6 address family, Cisco-like configuration, the BGP table, TCP improvements, and many more. The quality of the model is ensured by a close comparison of all aspects of the model to Cisco's implementation of BGP.

Sabína Gulčíková
finite memory automata, register automata, regular expression matching
Testování, analýza a verifikace
Register automaton (RA) operating over an infinite alphabet is one of the great tools for pattern matching with backreferences, runtime verification, or modelling of parallel computation. In case of pattern matching with backreferences, the state-of-the-art matchers make use of backtracking algorithms, whose application causes significant slowdown in case of nondeterministic regular expressions. The RA's property of non-determinisability makes it an unsuitable model for solution to problems related to inefficient usage of backtracking algorithms. On the other hand, the RA's quality of being equipped by a finite memory serves as a~good basis for storing the so-called capture groups used in this application. In this work, a~formal model called register set automaton is proposed. A large class of RAs can be transformed into this deterministic model, which, among other things, allows for fast pattern matching with backreferences. In this paper, we explore its properties including determinisability, expressive power, and closure under Boolean operations. In addition, algorithms for other problems, such as emptiness testing, are introduced.

Petr Kohout
bioinformatika, proteinové inženýrstvı́, molekulárnı́ dynamika, tunely, dokovánı́
Tato práce se zabývá analýzou proteinových struktur. Cílem je vytvořit Caver Web 2.0 - novou verzi webové aplikace, která začlení další vědecké nástroje a uživatelům umožní projít komplikovaný pracovní protokol za poskytnutí relevantních výsledků bez nutnosti hlubší znalosti integrovaných nástrojů. Vše bude zprostředkováno prostřednictvı́m jednoduchého a interaktivnı́ho uživatelského rozhranı́. Aplikace rozšiřuje původnı́ aplikaci Caver Web 1.0 o nové vlastnosti. Caver Web 1.0 je webový server vhodný pro identifikaci proteinových tunelů a kanálů, pro které umožňuje spustit analýzy transportu ligandů. Program se vyznačuje intuitivnı́m a uživatelsky přı́větivým rozhranı́m s minimem požadovaných vstupů od uživatele. Server je vhodný i pro výzkumnı́ky bez pokročilých bioinformatických nebo technických znalostı́. Jeho současná verze je ve vědecké komunitě dobře zavedená a velmi využı́vaná (35 000 dokončených výpočtů během dvou let provozu). Nejvýznamnějšı́m omezenı́m současné verze je možnost analyzovat pouze statickou strukturu, což často poskytuje neúplný biologický obraz. Proto jsme se rozhodli nástroj rozšı́řit o výpočet molekulárnı́ch dynamik, které poskytnou ucelený obraz na proměny proteinových struktur. Touto funkcı́ se Caver Web 2.0 stane prvnı́m webovým nástrojem, který bude poskytovat analýzu tunelů bez nutnosti ručnı́ch výpočtů molekulárnı́ch dynamik. Grafické uživatelské rozhranı́ bude navrženo speciálně pro vědeckou komunitu s podporou jednoduchého exportu. Nástroj bude zdarma k dispozici celé vědecké komunitě.

Tomáš Hladký
Simulator, DAG-based consensus, Blockchain, Optimizations, Payoff function, Transaction throughput
Bezpečnost
We study existing Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) blockchain designs that propose to solve a blockchains throughput problem, especially protocols PHANTOM and its optimization GHOSTDAG. They utilize a Bitcoin protocol and propose a random transaction selection, resulting in increased transaction throughput. However, it has been proved by a simulation that actors that use the random transaction selection strategy have less profit than actors who do not follow the protocol and select transactions rationally (i.e., most profitable). That proof has been made on a small network of ten nodes with a circle topology. This article aims to extend, optimize, and automate an existing blockchain simulator. We implement a Bitcoin-like network topology with realistic block propagation latency. Furthermore, we optimize the simulator to run more simulations in parallel and faster, including automation tools that can create or edit input configurations, perform a combination of runs on multiple CPUs based on input parameters, and analyze profits and transaction collisions. Finally, we perform experiments to verify malicious actors' advantages in a Bitcoin-like network and create a payoff function to punish this behavior.